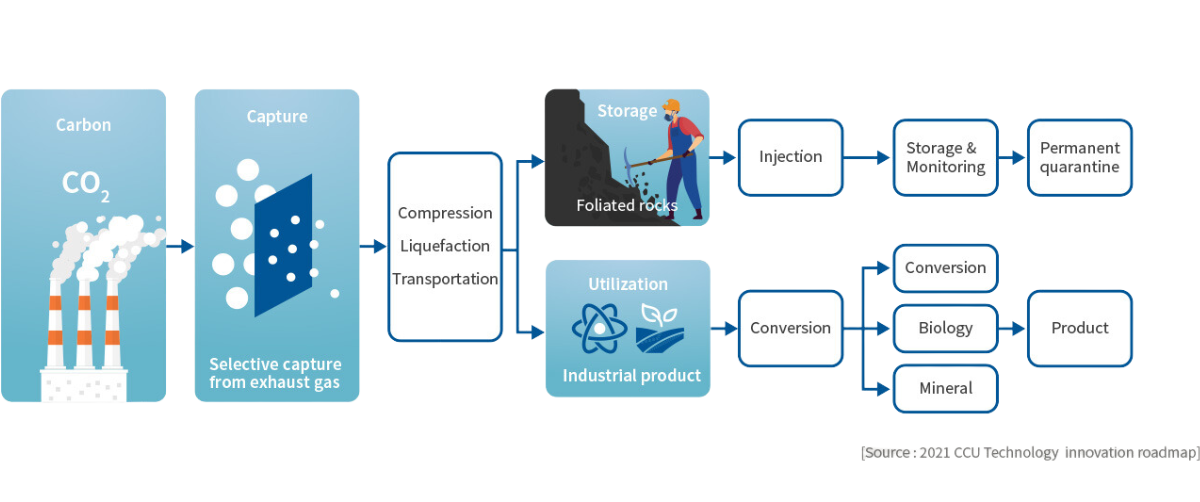
CCUS is a technology that prevents carbon dioxide from being emitted into the atmosphere at the production
source (Carbon Capture) and uses it where necessary (Utilization) or stores it underground (Storage).
2030 NDC : Committed to reducing CO2 emissions by 40% compared to 2018 by 2030 (Declared in
COP26)
The IEA (International Energy Agency) judges that the CCUS Technology is the most feasible.

After collecting CO2 from plants, it is transferred to supercritical fluid by applying a pressure of 80 to 100 bar. Then, CCS technology means spraying and isolating oil and gas layers and salt water layers located 800 to 1,000 meters underground. If storage locations are difficult to secure, the captured CO2 can be liquefied and used in welding, smart farms, or converted into other useful materials. CO2 conversion methods include mineralization, microalgae, and chemical methods.
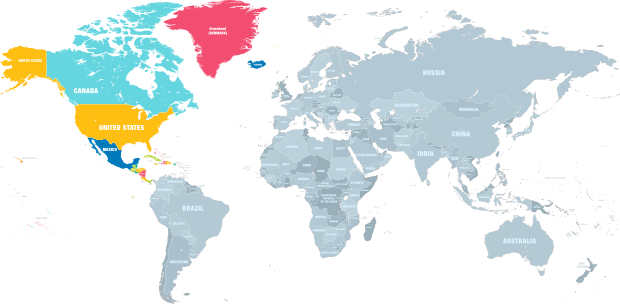
Global CO2 HUB Construction status
- Total : 64HUB
- In operating : 26
- Under construction : 4
- Design stage [feed] : 13
- Development stage : 21
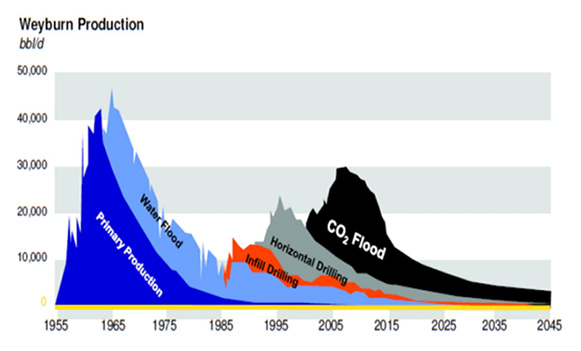
Example of the yield from EOR
Incremental recovery 155 MMbbls
Sequestration 45 million tonnes CO2