NEW TECHNOLOGY
Total Solution
STICO Lab is advancing several carbon capture and storage opportunities around the world to help support our commitment to the Paris Agreement.

Capture – Storage Scenario
Methodological Limitations

-
EOR (Enhanced Oil Recovery)
- • Overseas distribution problems (war, virus, diplomacy, etc.)
- • Increase in demand (CO2 gas) compared to supply (place)

-
CO2 HUB
- • Geological space limitation
- • NIMBY (Not in my backyard)
- • Safety issues such as explosions
Our Future Plan for Net-Zero CO2
New Industries using CO2
Floating CCUS Plant
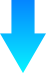
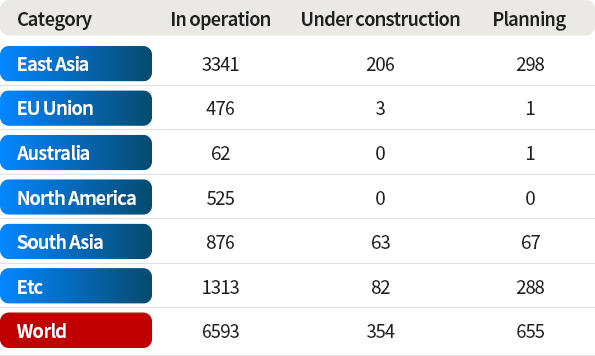
Global Coal Power Plant
CO2 Capture Plant Market Size
$ 2.8 trillion
(KRW 3,000 trillion)
$ 10 trillion or more
(Including Chemical / Cement / Steel Industry)
• Capture - Utilization
• Carbon Mineralization
Build of Green Energy
Global Marine Fuel Market Size
$ 100 billion per year
(KRW 120 trillion)
H2 from Seawater Electrolysis
CO2 from Industrial Plant

• Methanol / Hydrogen Fuel
• Industrial Power Supply
Dual-Carrier Ship Operation
Domestic CO2 Transport Market Size
$ 18 billion per year
(KRW 20 trillion)
Limitations of Domestic CO2
export for EOR Utilization

• Use in Methanol Production
• EOR
Floating CCUS Plant
Utilization of world-class domestic shipbuilding technology – Floating CO2
Capture
Plant (250MW, 500MW, 1000MW)
Reduced construction cost by 1/5 compared to onshore plants – Preoccupation in the
global market
Construction Investment Cost : 250MW - $200 million / 500MW - $400million / 1000MW -
$700million
• Coal-fired power plants around the world : 7,000 unit (Operating + Under Construction)
• Average construction cost of floating CO2 capture plant : $ 400 million (Based on 500MW)
• Market size : 7,000 Unit x $ 400 million / unit $2.8 trillion (KRW 3,000 trillion)
• 10% Market share $280 billion (KRW 300 trillion)

Floating Combined Cycle Power Plant
Build of Green Energy
World shipping companies – To order 50 methanol vessels by the end of this
year
UK CLARKSON predicts that by 2030 75-80% of the world's ships will use methanol fuel
National hydrogen industry development policy – 30 million tons of hydrogen
production per year
Green Energy from Seawater with CO2
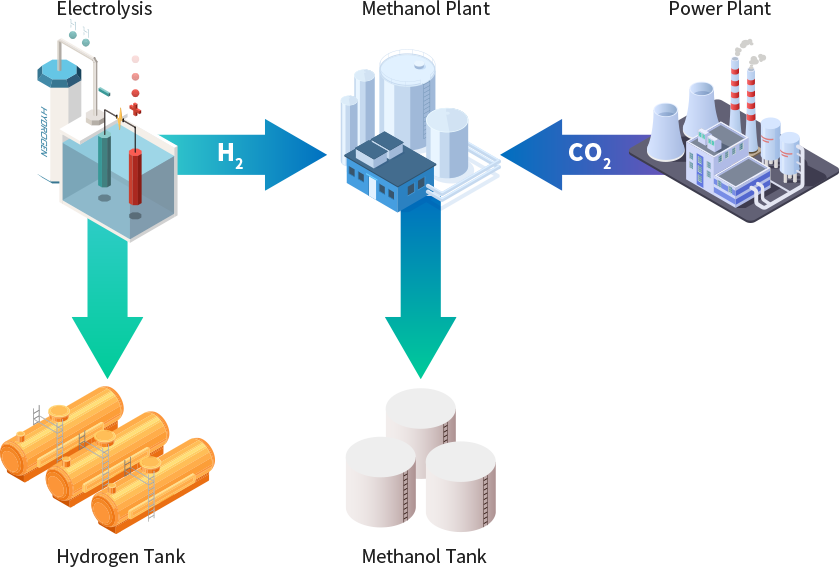
World-Class Methanol / Hydrogen Fuel Supply
Hydrogen produced through seawater electrolysis can be used as new energy and can be converted into methanol through a chemical reaction with carbon dioxide. Green methanol and recycled methanol technology, which converts large amounts of carbon dioxide generated in chemi-cal plants, power plants, and steel mills directly into methanol without syngas, are expected to contribute to responding to climate change. Methanol is used as a synthetic solvent as well as a raw material for the manufacture of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals. It is also used as a clean raw material for shipping ships and as fuel for methanol fuel cells.
“ Methanol will lead the world in the future ”
Beyond Oil and Gas : The Methanol Economy


As the shipbuilding industry is accelerating the development and commercialization of next-generation eco-friendly fuel for ships that will follow liquefied natural gas (LNG), ‘methanol-powered ships’, which will serve as a stepping stone before the full-fledged offshore hydrogen market, are gaining momentum. Recently, as global shipping companies are increasing orders for large container ships that use methanol as fuel, competition for orders for methanol-powered ships is intensifying.
Previously, Musk, a world-class large shipping company, placed an order to Hyundai Heavy Industries in August 2021 to build eight 16,000 TEU container ships that use methanol as fuel by 2024 by 2024. Along with Musk, CMA CGM, a global 'top 3' shipping company, recently announced a plan to place an order for six new 15,000 TEU-class methanol dual-fuel new ships.
Dual – Carrier Ship Operation
Captures 300 million tons, about 50% of Korea’s annual CO2 emissions → Requires 500 carriers
Expected boom in domestic shipbuilding and steel industry
Annual CO2 emissions in Korea
680 million tons (as of 2021)

CO2 Storage - Utilization
300 million tons (as of 2021)

Dual-Carrier (CH3OH/H2/CO2)
- Average voyage time : 1 time / 60 days → 6 times / year
- Average CO2 transport volume : 100,000 tons / time
- Number of ships to transport 300 million tons of CO2 : 500 unit
- Construction cost per ship : $ 100 million → Total $ 50 billion
- Annual freight revenue : $ 18 billion
CCUS Total Solution
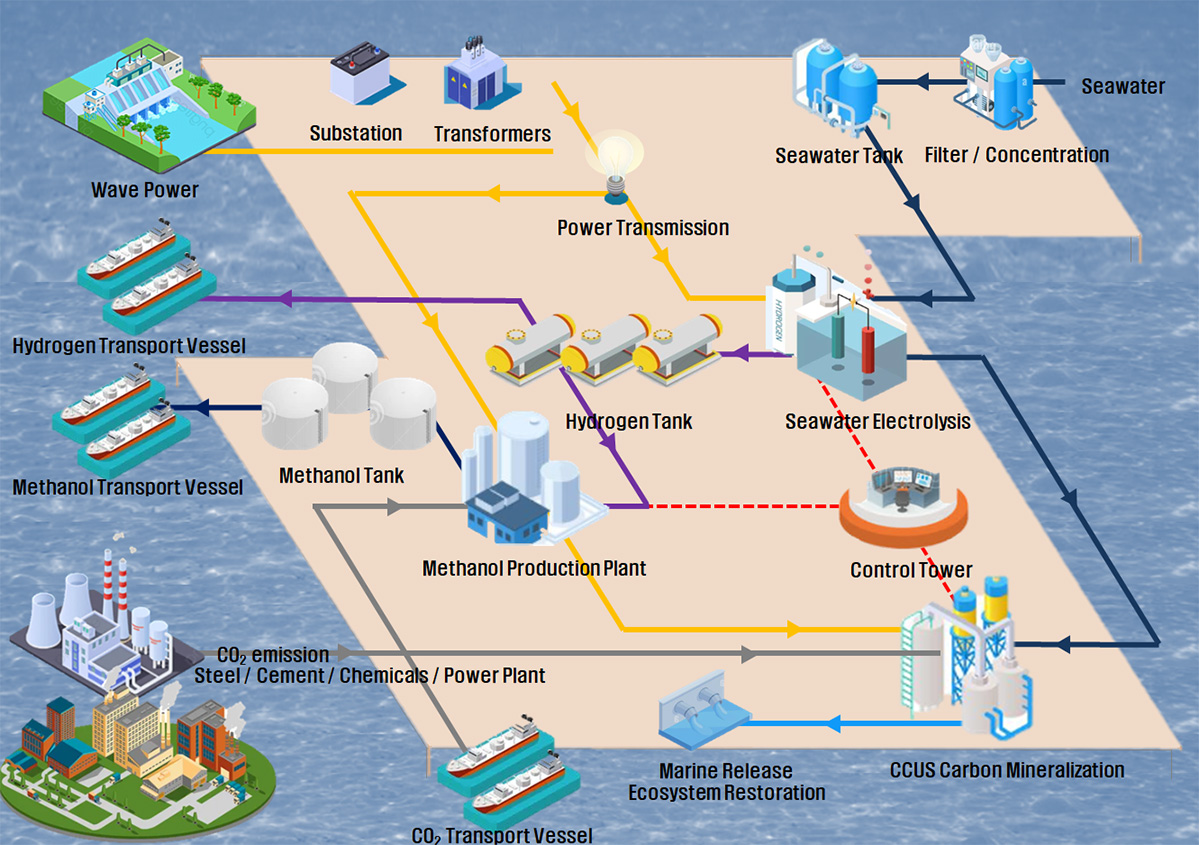
Element technology: Wave power renewable energy using seawater / Hydrogen new energy through electrolysis / Methanol production through the synthesis of hydrogen and carbon dioxide / Carbon mineralization through the reaction of seawater and carbon dioxide / Ocean alkaliza-tion and ecosystem restoration through carbonate discharge
CCUS Technology Applied to ships
Responding to GHG (Green House Gas) emission regulations of IMO (International Maritime Organization)
The IMO aims to reduce ship GHG emissions by 50%
compared to 2008 levels by 2050
Current Marine CCUS Technology



- • Energy consumption for continuous use of absorbent
- • Absorbent toxicity, explosion hazard
- • Space occupancy due to process complexity
- • CO2 liquefied storage facility
- • Network process required for carbon dioxide transport
- • Expensive maintenance cost
Future Marine CCUS Technology



Seawater contains about 3.4 ‰ of salt. The seawater flowing into the electrolysis device installed on the ship reacts to generate metal hydrox-ide. A stable form of carbonate is produced through the reaction of the seawater containing the metal hydroxide prepared in this way with the carbon dioxide emitted from the ship stack. Carbonate generated through these chemical reactions becomes a resource that can restore the marine ecosystem by re-discharging it to the sea without the need for a separate storage facility.
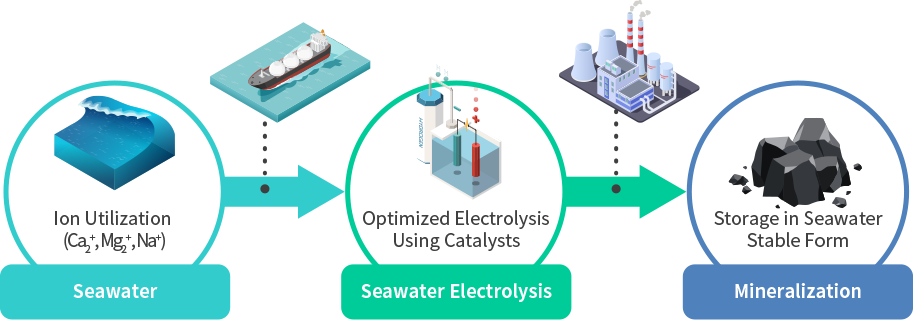
When using 1 / 1,000,000 seawater in earth, 23.7 billion tons of CO2 reduction
The best way to achieve Net CO2 Zero
Currently, policies for reducing carbon dioxide in ships, a source of non-road pollution, focus on the production and utilization of liquefied carbon dioxide through the absorption-desorption regeneration process. However, considering space constraints, excessive energy consump-tion, economic feasibility, human harm and risk, We propose technology that can contribute to the marine ecosystem is more suitable.
